A new study by Atlas VPN revealed that Apple makes the highest payout in bug bounty rewards to researchers for finding and reporting software vulnerabilities across its devices. In comparison to Samsung, Apple’s bug bounty rewards are 5x more than its rivals.
But even then, the Cupertino tech giant faces criticism from developers or security researchers for not crediting their discoveries and not paying the rewards.

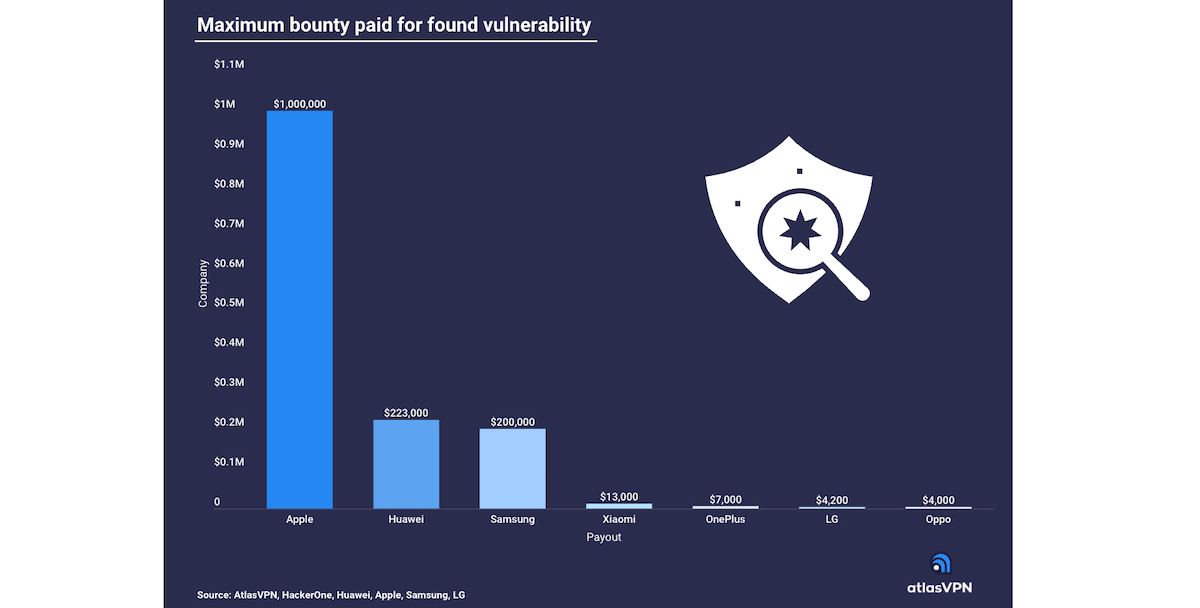
Apple pays the highest bug bounty rewards from $100K to $1 million to researchers to find exploits
As per the report, the Cupertino tech giant can pay up to $1 million for discovered exploits in its devices which is a great incentive for security researchers to hunt for vulnerabilities in Apple software operating systems. Huawei pays the second-highest amount in bug bounty rewards up to $223 thousand for exploits in its AppGallery, cloud services, or the phones themselves. And Samsung stands in third place with up to $13 thousand payouts for exploits.
- Apple pays from $100K to $1 million to researchers who find exploits in their devices. Our report from earlier in the year found that vulnerabilities in Apple products surged by over 450%.
- Huawei’s bug bounty program offers payouts from $200 to $223K for found vulnerabilities in their devices.
- Samsung’s bug bounty program rewards researchers between $200 and $200K for qualified exploits depending the severity level, vulnerability report quality, affected scope, and the difficulty of attacks.
- Xiaomi bounty payments range from $800 to $13K for found vulnerabilities and has a special Hacker Leaderboard reward, for hacker who earned the most bounty on Xiaomi’s program.
- OnePlus and Oppo, both owned by BBK Electronics, bug bounty programs can reward researchers with up to $7K and $4K, respectively.
- The LG bug bounty program offers compensation of up to $4.2K based on the severity of security vulnerability.
However, several security researchers registered with Apple Security Bounty (ASB) program have expressed dissatisfaction and frustration with the management of the program. Researchers complain that the company takes months to respond to submitted vulnerabilities and sometimes, patches the discovered vulnerabilities without crediting the bug hunter and giving their due reward.
This behavior was evident in the case of developer Denis Tokarev who discovered four zero-day exploits. Apple patched on iOS 14.7 without giving him credit and when he went public with the remaining three exploits in iOS 15, the company superficially apologized to do the same later. In iOS 15.0.2 update, the company fixed a gaming zero-day exploit without giving Tokarev credit and cash rewards. Two more exploits still remain to be fixed, the exploits were submitted between March-May 2021.
Some disgruntled have also pondered over selling the exploits to vendors like HackerOne, Zero Day Initiative, or third-party which could be firms like NSO, creator of Pegasus spyware to hack iPhone and Android devices.