Environment variables on Windows 11 are dynamic named values that store information about the operating system, the current user, and the current process. They can be used to control the way that programs behave and to provide information to the operating system.
Environment variables are used by both graphical and command-line programs. For example, the PATH environment variable tells the operating system where to look for executable files when you type a command in a command prompt window. The TEMP environment variable tells the operating system where to store temporary files.
Environment variables can be either system variables or user variables. System variables are available to all users on the computer, while user variables are only available to the current user.
Here are some examples of how environment variables are used:
- The PATH environment variable is used by the operating system to find executable files when you type a command in a command prompt window.
- The TEMP environment variable is used by the operating system to store temporary files.
- The TMP environment variable is the same as TEMP, but it is used by older programs.
- The USERNAME environment variable contains the name of the current user.
- The HOMEPATH environment variable contains the path to the current user’s home directory.
You can also create your own environment variables to store custom settings for your programs or scripts.
Environment variables can be a powerful tool for controlling the way that your computer works. However, it is important to be careful when changing environment variables, as incorrect changes can cause problems with your computer.
In this guide, we will show you how to create Environment Variables in Windows 11.
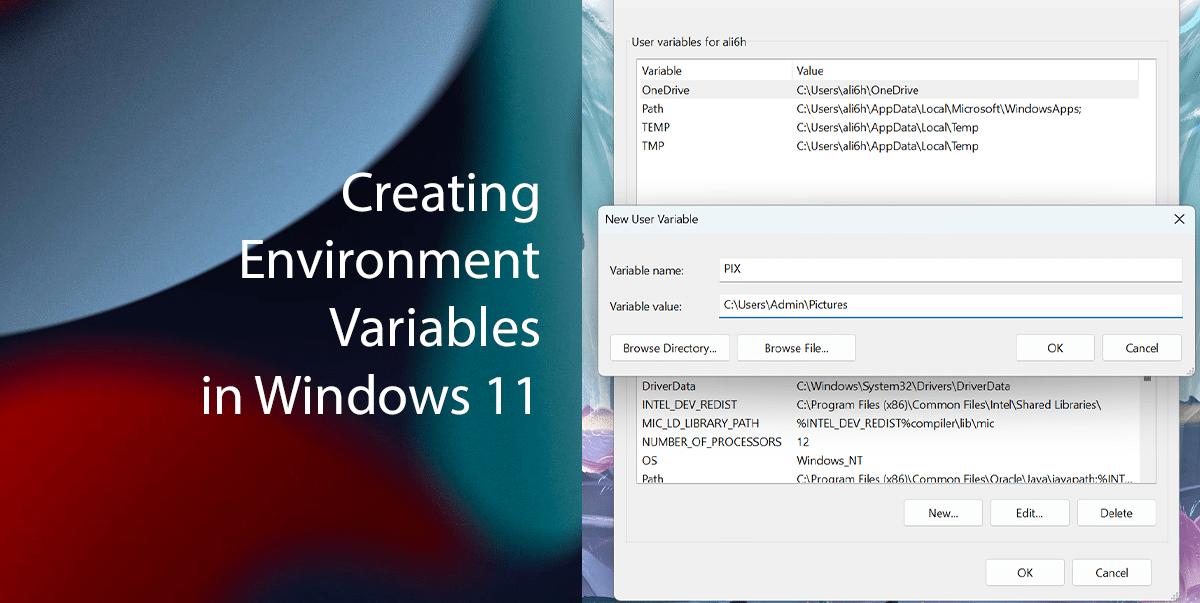
Here is the easiest way to create Environment Variables in Windows 11
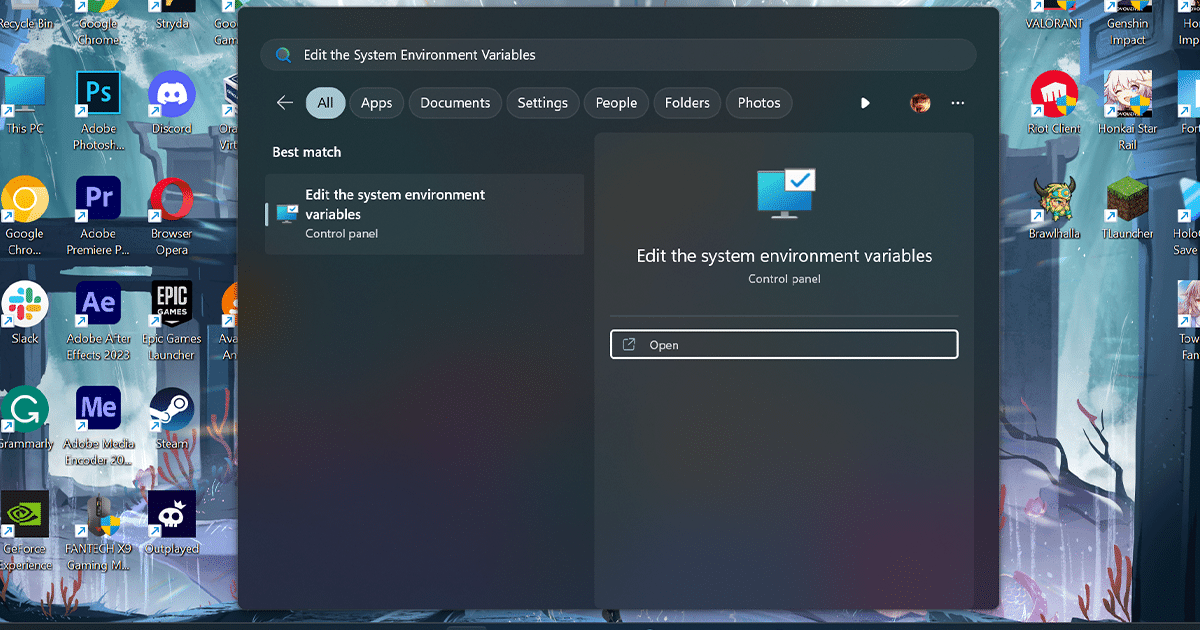
- Open Start, search for Edit the System Environment Variables, and click the Open button.
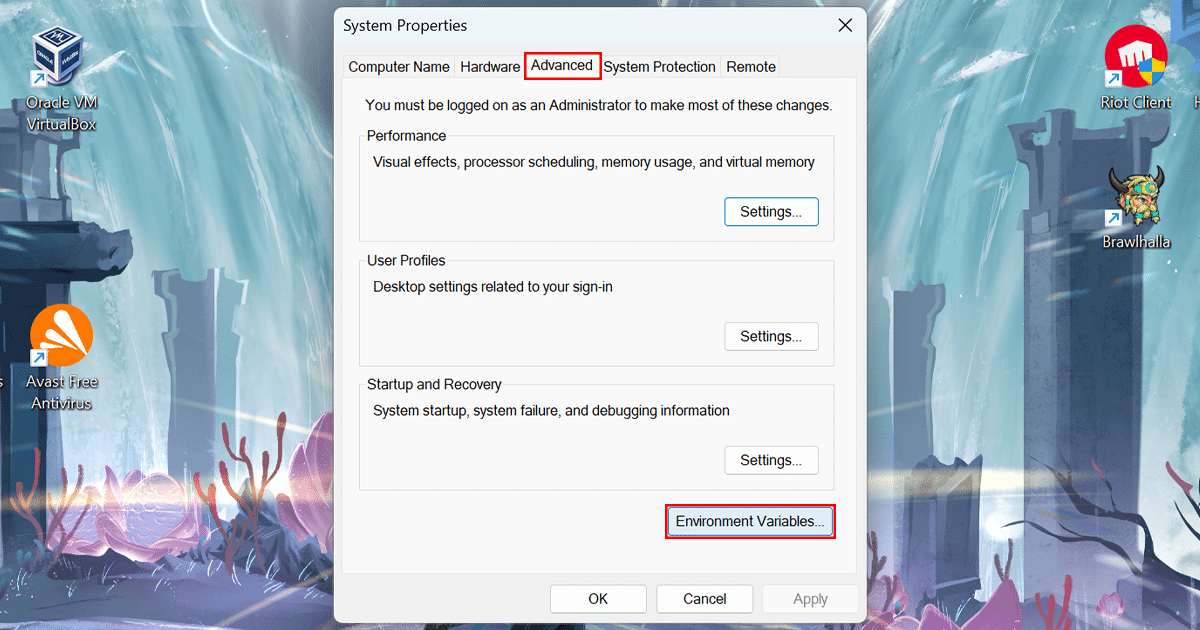
- Click the Advanced tab and click the Environment Variables button.
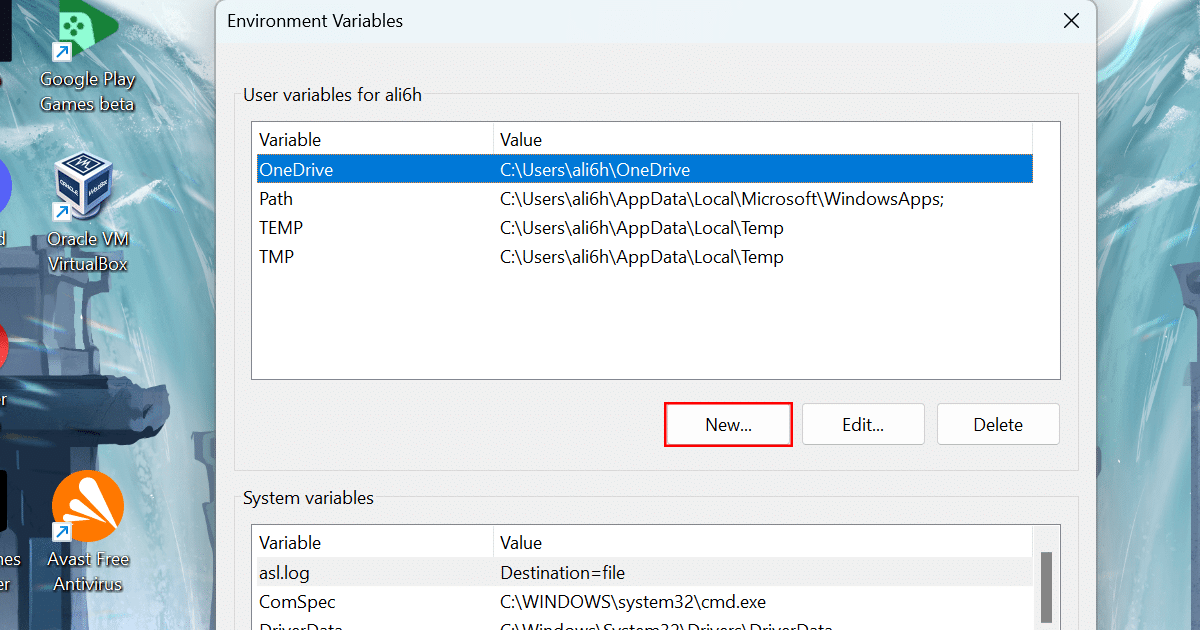
- Under the “User variables for admin” section, click the New button.
- In the Variable name field, confirm the name for the variable. For example, “PIX.”
- In the Variable value field, confirm the path for the folder, drive, or file to open with the new variable. For example, “C:\Users\Admin\Pictures.”
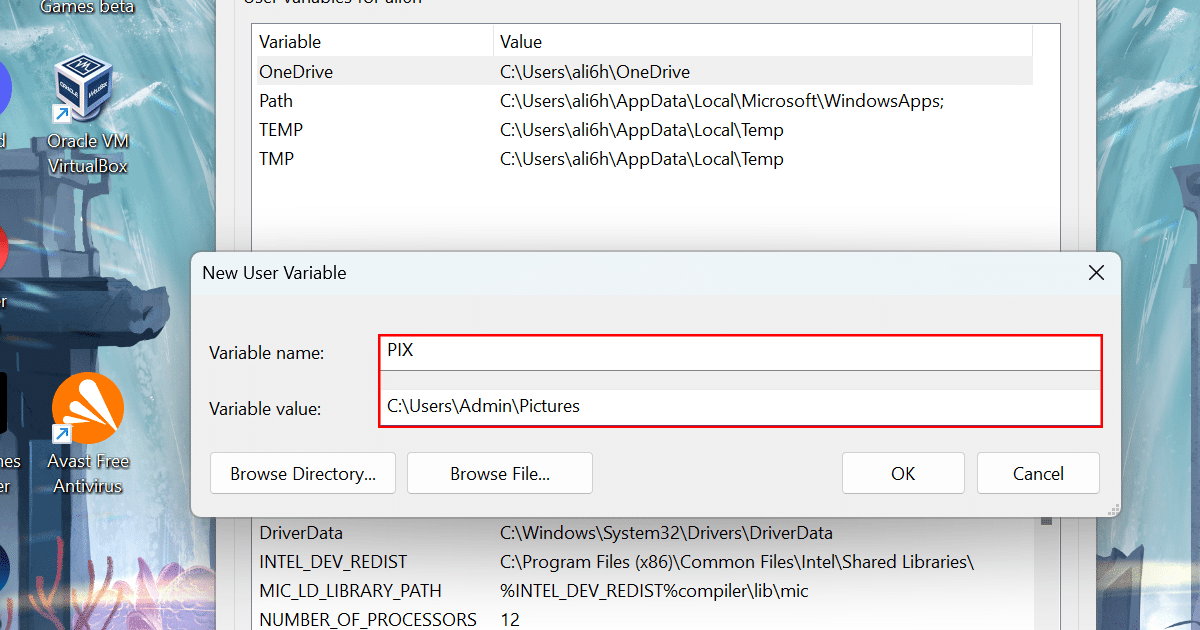
- Click the OK button and click the OK button again.
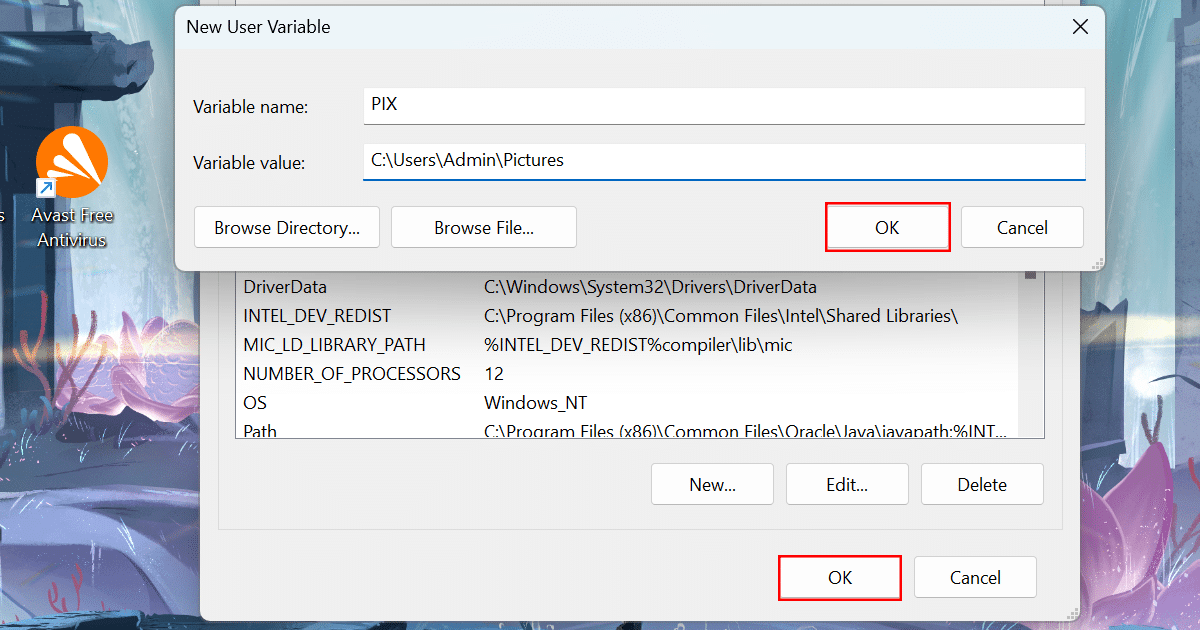
- When done, the system will create a new variable, and you can use it to access the specific location or file with the variable.
Read more: