Apple is rolling out the first public release of the Rapid Security Response update to all iOS and macOS users. The new iOS Security Response 16.4.1 (a) and macOS Security Response 13.3.1 (a) updates are now available on all compatible devices.
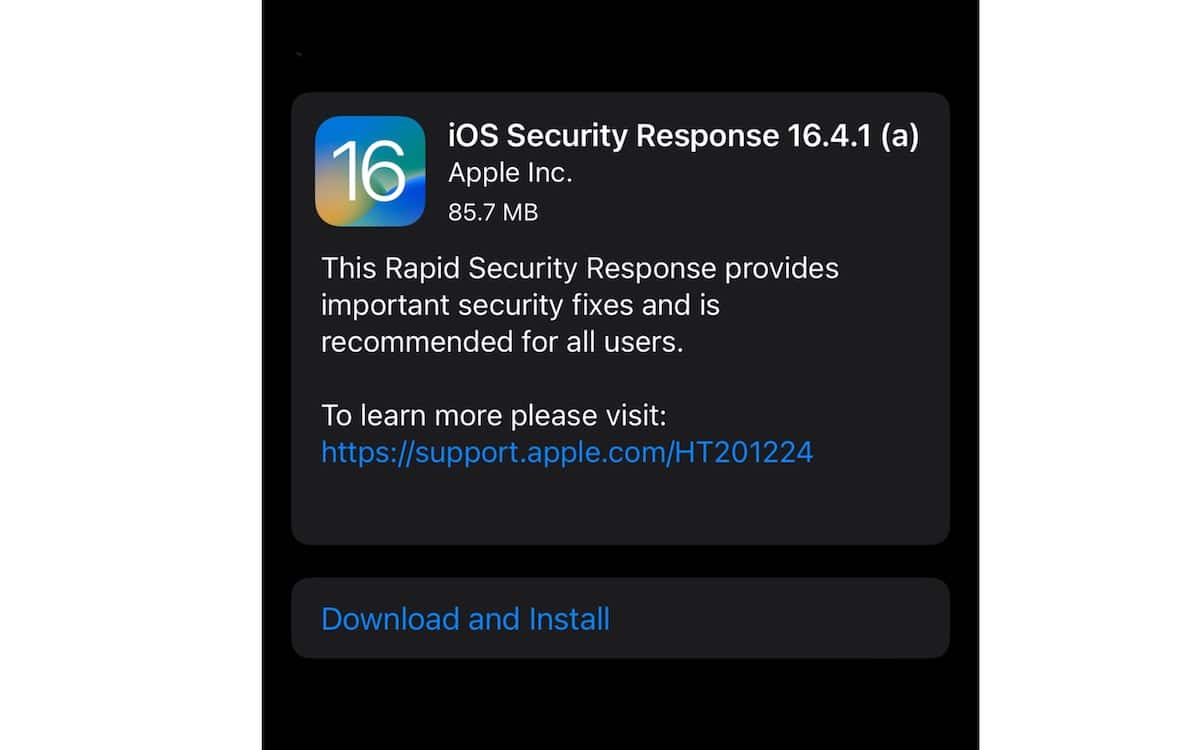
In October 2022, the tech giant announced the Rapid Security Responses updates to only release security fixes to users more frequently in future iOS, iPadOS, and macOS updates without releasing a full OS update.
Apple first introduced Rapid Security Response 16.4 (a) update and macOS Security Response 13.3 (a) in iOS 16.4 beta 2, and a few days later, the company released Rapid Security Response iOS 16.4 (b).
However, during its beta testing phase, the updates did not include release notes which list new features. Now, the public version of the Security Response update for iOS and macOS also does not feature release notes to detail which exploit it patches.
How to download the Rapid Security Response update for iOS 16.4.1 and macOS 13.3.1
As Apple has made the new Rapid Security Responses available with iOS 16.4.1, iPadOS 16.4.1, and macOS 13.3.1., users must make sure that their devices are updated to the latest iOS and macOS version.
To install the updates, the need to take the following steps:
On iOS and iPadOS
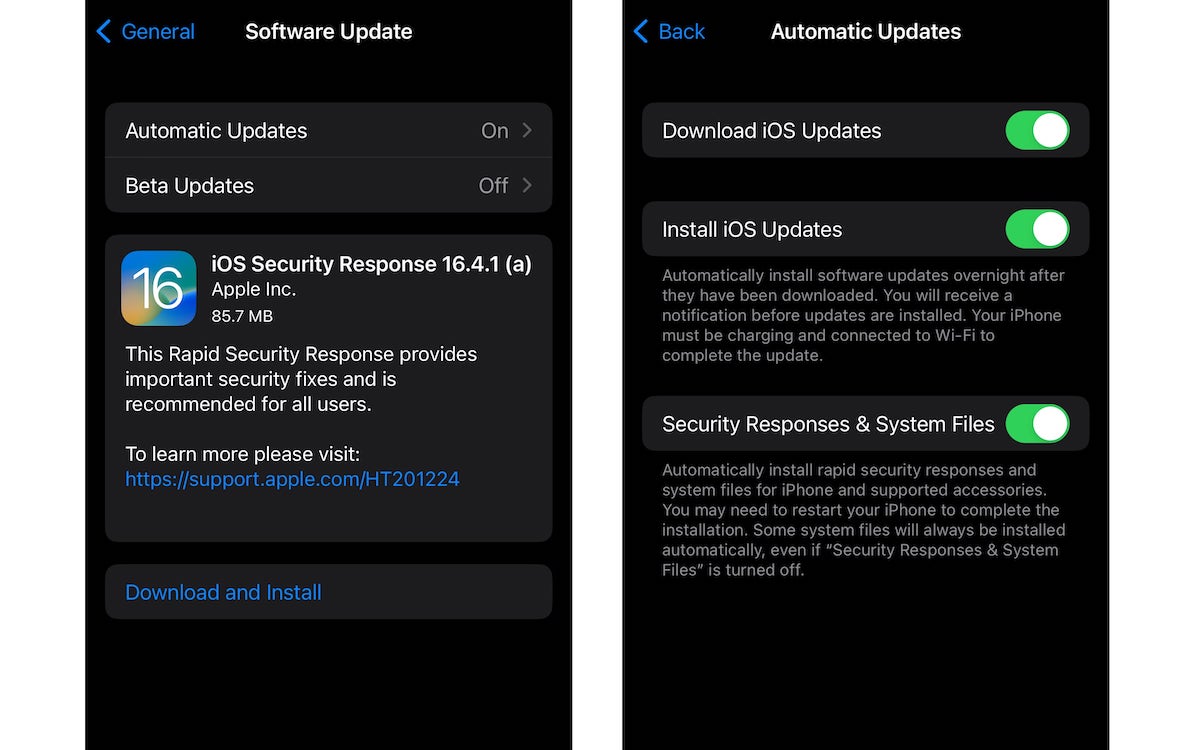
- Open Settings > General > Software Updates
- Tap on the “Automatic Updates” option and turn on the ‘Security Responses & System Files’ feature
On macOS
- Click on System Settings > General > Software Update
- Click on the “Automatic Updates” option and turn on the “Install Security Responses and system files” feature
When the feature is enabled in iOS and macOS, the Security Response updates appear in the “Software Update” section.
- Simply select the “Download and Install” button to install it.
As the tech giant details that the new Security Responses deliver important security improvements, users must download them as soon as they can.
Rapid Security Responses are a new type of software release for iPhone, iPad, and Mac. They deliver important security improvements between software updates — for example, improvements to the Safari web browser, the WebKit framework stack, or other critical system libraries. They may also be used to mitigate some security issues more quickly, such as issues that might have been exploited or reported to exist “in the wild.”
Read More: